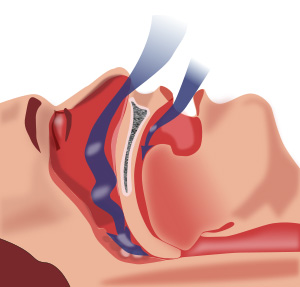
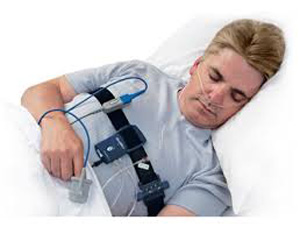
In non-sleepy patients with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), treatment with continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) can reduce the incidence of cardiovascular events and hypertension, according to researchers from Spain.
The research will be presented at the ATS 2010 International Conference in New Orleans.